SLL's embedded software innovation has been recognised by our customers and partners. Major FPGA, memory, and development board makers now officially partner with SLL. This ensures SLL IP is validated on a wide range of physical devices. SLL customers are located in most geographical regions, and include Fortune Global 500's, government agencies, and SME's from USA and Canada to China.
Unleash NOR Flash Performance: Synaptic Laboratories IP Maximizes DDR x8 Throughput on FPGAs
In our world of embedded systems and configurable computing, fast and reliable boot times are paramount.
Increasingly, developers are turning to NOR flash memory for storing firmware, configuration data, and even application code intended for direct execution. While NOR flash offers advantages like non-volatility, random access, and code shadowing capabilities, achieving optimal performance, especially when dealing with complex data streams, can be a challenge. That’s where Synaptic Laboratories Ltd (SLL) comes in.
SLL has developed a groundbreaking Intellectual Property (IP) core specifically designed to unlock the full potential of high-speed NOR flash configurations within the fabric of an FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array). Their IP empowers developers to harness the exceptionally high throughput offered by a 200 MHz DDR (Double Data Rate) x8 configuration NOR flash, resulting in significantly improved run-time performance after system boot. This post will delve into the technical details, exploring the benefits of this SLL innovation and explaining why it’s becoming essential for applications demanding peak performance from their flash memory.
Understanding the Bottleneck: NOR Flash Performance Limitations
Traditional approaches to interfacing with NOR flash memory can often become a performance bottleneck. While the flash itself might boast impressive specifications, the interface logic implemented within an FPGA, without optimized IP, may struggle to keep pace. This can lead to suboptimal data transfer rates and ultimately impact overall system performance. Several factors contribute to this limitation:
- FPGA Logic Complexity: Designing custom logic to handle complex NOR flash protocols, including DDR, requires significant FPGA resources and development time. This can be a costly endeavor, both in terms of time and silicon utilization.
- Timing Constraints: Meeting the tight timing constraints required for high-speed DDR operations can be extremely challenging within the FPGA fabric. Factors like signal propagation delays and clock jitter can significantly impact data integrity and overall throughput.
- Protocol Overhead: Standard NOR flash protocols often involve significant overhead, including address latching, command sequences, and wait states. This overhead can reduce the effective bandwidth available for data transfer.
- Interrupt Latency: In many embedded systems, data transfer from NOR flash is triggered by interrupts. The latency associated with interrupt handling can further impact performance, especially when dealing with time-critical applications.
The SLL Advantage: Optimized IP for Peak NOR Flash Performance
Synaptic Laboratories Ltd.’s IP core addresses these challenges head-on, providing a pre-verified and highly optimized solution for interfacing with 200 MHz DDR x8 NOR flash memories within an FPGA. The core focuses on several key areas to maximize throughput and minimize latency:
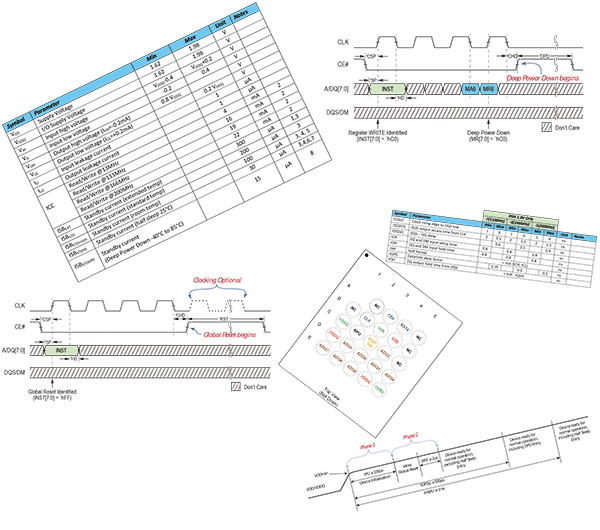
- High-Speed DDR Interface: The SLL IP is meticulously engineered to meet the stringent timing requirements of DDR operation. It leverages advanced FPGA features, such as dedicated I/O blocks and phase-locked loops (PLLs), to ensure accurate data capture and transmission at the specified 200 MHz clock rate. The x8 configuration further amplifies the throughput by transferring 8 bits of data per clock cycle.
- Optimized Protocol Engine: The core incorporates a highly efficient protocol engine that minimizes overhead and streamlines data transfer. This engine intelligently manages address generation, command sequencing, and wait state insertion, ensuring that the flash memory is operating at its peak efficiency.
- Configurable Memory Mapping: The IP core allows developers to configure the memory map according to their specific application requirements. This flexibility enables efficient memory management and reduces the need for complex address translation logic.
- Advanced DMA Support: Integrated Direct Memory Access (DMA) functionality enables high-speed data transfer between the NOR flash memory and other peripherals or memory regions within the FPGA. DMA bypasses the CPU, significantly reducing processor load and improving overall system responsiveness.
- Error Detection and Correction: The SLL IP incorporates error detection and correction mechanisms to ensure data integrity, especially in harsh environments where the risk of bit errors is higher. This feature enhances the reliability and robustness of the system.
- FPGA Fabric Optimization: The IP core is designed to minimize resource utilization within the FPGA fabric. This allows developers to allocate more resources to other critical functions, such as signal processing or control logic.
- Comprehensive Verification: SLL rigorously verifies its IP core to ensure its functionality and performance across a wide range of operating conditions. This extensive verification process provides developers with confidence in the reliability and robustness of the solution.
Benefits of Using SLL IP for NOR Flash Integration
The advantages of using SLL’s IP for integrating 200 MHz DDR x8 NOR flash memory into FPGA-based systems are numerous and impactful:
- Increased Throughput: The primary benefit is a significant increase in data throughput compared to traditional NOR flash interfaces. This translates to faster boot times, improved run-time performance, and the ability to handle more demanding data streams.
- Reduced Latency: The optimized protocol engine and DMA support minimize latency, resulting in faster response times and improved system responsiveness.
- Simplified Development: The pre-verified IP core simplifies the development process, reducing the time and effort required to integrate NOR flash memory into the system.
- Lower Development Costs: By using SLL’s IP, developers can avoid the costly and time-consuming process of designing custom logic for NOR flash interfacing.
- Reduced FPGA Resource Utilization: The optimized IP core minimizes resource utilization within the FPGA fabric, allowing developers to allocate more resources to other critical functions.
- Improved System Reliability: The error detection and correction mechanisms enhance the reliability and robustness of the system, ensuring data integrity.
- Faster Time-to-Market: The availability of a pre-verified and highly optimized IP core enables developers to bring their products to market faster.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The configurable memory mapping and DMA support provide the flexibility to adapt the IP core to a wide range of application requirements.
Applications Benefiting from Enhanced NOR Flash Performance
The SLL IP core is particularly well-suited for applications that demand high throughput and low latency from their NOR flash memory:
- Embedded Systems: Faster boot times and improved run-time performance are critical for embedded systems, especially those used in real-time control and data acquisition applications.
- Industrial Automation: Industrial automation systems often rely on NOR flash memory for storing configuration data and firmware. The SLL IP can significantly improve the performance of these systems, enabling faster response times and increased productivity.
- Medical Devices: Medical devices often require fast boot times and reliable data storage. The SLL IP can help to ensure that these devices meet the stringent performance requirements of the medical industry.
- Telecommunications: Telecommunications equipment often relies on NOR flash memory for storing firmware and configuration data. The SLL IP can significantly improve the performance of these systems, enabling faster data transfer rates and increased network capacity.
- Aerospace and Defense: Aerospace and defense applications often require high-performance and reliable data storage. The SLL IP can help to ensure that these systems meet the stringent requirements of these industries.
- Software Defined Radio (SDR): SDR applications often require the storage and retrieval of large amounts of data in real-time. Utilizing SLL’s IP for NOR Flash can drastically improve the performance of these applications.
Conclusion: SLL IP – A Key Enabler for High-Performance FPGA-Based Systems
In conclusion, Synaptic Laboratories Ltd.’s (SLL) IP core provides a powerful and efficient solution for unlocking the full potential of 200 MHz DDR x8 NOR flash memory within FPGA-based systems. By addressing the limitations of traditional NOR flash interfaces, the SLL IP enables developers to achieve significantly higher throughput, reduced latency, and improved overall system performance. Whether you are developing embedded systems, industrial automation equipment, medical devices, or telecommunications infrastructure, SLL’s IP can help you to unleash the power of NOR flash memory and create innovative, high-performance products. If you’re struggling to get the performance you need from your NOR Flash implementation, considering leveraging pre-verified IP from companies like SLL can save significant development time and resources, while ultimately leading to a superior product.
SLL is the only specialist, dedicated xSPI SIP design house since 2016. XSPI SIP design and support is SLL core business, for FPGA and ASIC. Visit our website to learn about SLL’s highly innovative xSPI SIP portfolio that is already successfully used by global customers including Fortune Global 500’s, and in 100m+ volume ASIC projects.